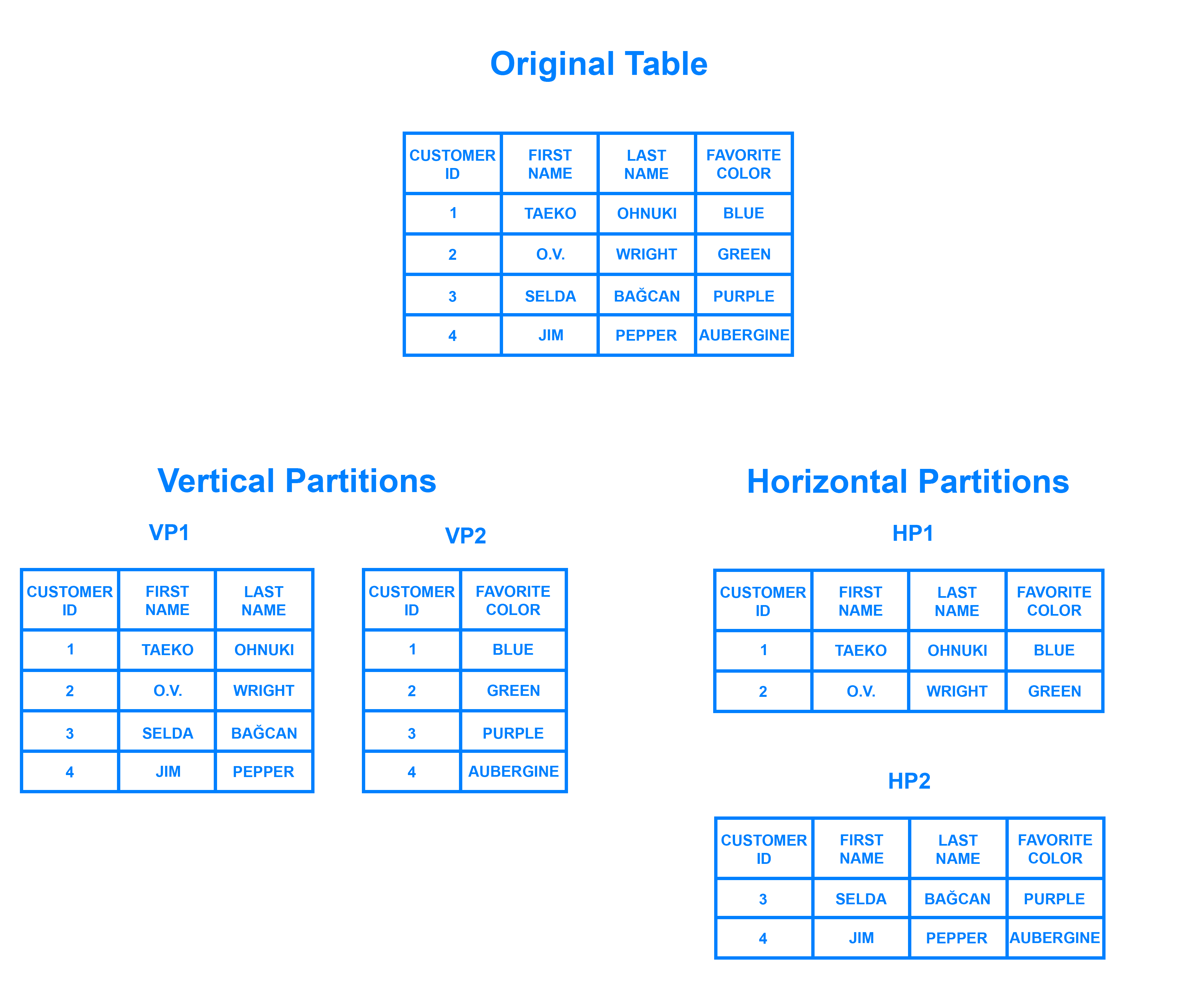

Data files or tables are parsed into smaller units. This is also called ‘partitioning’. A partition is usually performed against a primary attribute that is common across all the records, for example a date. We can partition files before or after we move the source files and tables to the cloud. This will depend on many factors, but often it is easier to migrate data to the cloud than parse it with glue or other tools in the raw object store.
Let’s assume you have a 10 GB file, and the default block size is 128 MB. We can calculate the number of partitions:
File Size in MB:
2. Number of Partitions:
So, for a 10 GB file, there would be 80 partitions. Using this calculation we can develop both code and logic; and the underlying infrastructure to support processing, including parallel processing.